On December 3, 2015, the U.S. Census Bureau released its 2010-2014 American Community Survey (ACS) 5-year estimates. The ACS collects information such as ancestry, educational attainment, income, employment, and housing characteristics and makes this data available at multiple geographic levels, including municipality and township. This release of the ACS marks the first time that users and analysts are able to compare two non-overlapping 5-year ACS datasets (2005-2009 and 2010-2014), and the first time that many of the region's smaller communities will be able to see this change for their jurisdictions. This Policy Update is part of a series that uses the most recent ACS data to examine broad trends in the CMAP region.
Beginning in 2011, the baby boom generation (those born between 1946 and 1964) began to age into the senior demographic. As this generation continues to age, residents age 65 and over will represent a growing proportion of the nation and region's population. According to GO TO 2040, the number of residents between 65 and 84 years of age is projected to double by 2040. While this growth is currently occurring most strongly in the region's inner region suburbs and exurban areas, much of the region is seeing an increase in senior residents. This phenomenon will have major impacts on future housing, land use, and transportation needs.
The U.S. Census Bureau's ACS 2010-2014 estimates are weighted rolling averages of 5-year periods. All references in the text to 2009 and 2014 are 2005-2009 or 2010-2014 ACS estimates, respectively. To assess trends in the region's senior population and update prior analysis, this Policy Update compares the most recent ACS estimates with data from the 2005-2009 ACS estimates. The update finds that the region's senior population is growing.
Regional patterns
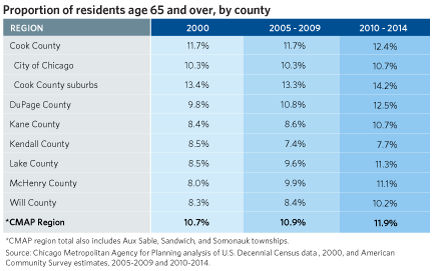
The latest ACS estimates indicate that the proportion of the northeastern Illinois population that are senior citizens is rising. This trend mirrors findings in previous CMAP analysis comparing 2000 and 2010 decennial census data. The following table shows that seniors have become a greater proportion of the population across all counties, with growth occurring more quickly in recent years as the proportion of baby boomers above age 65 increases.
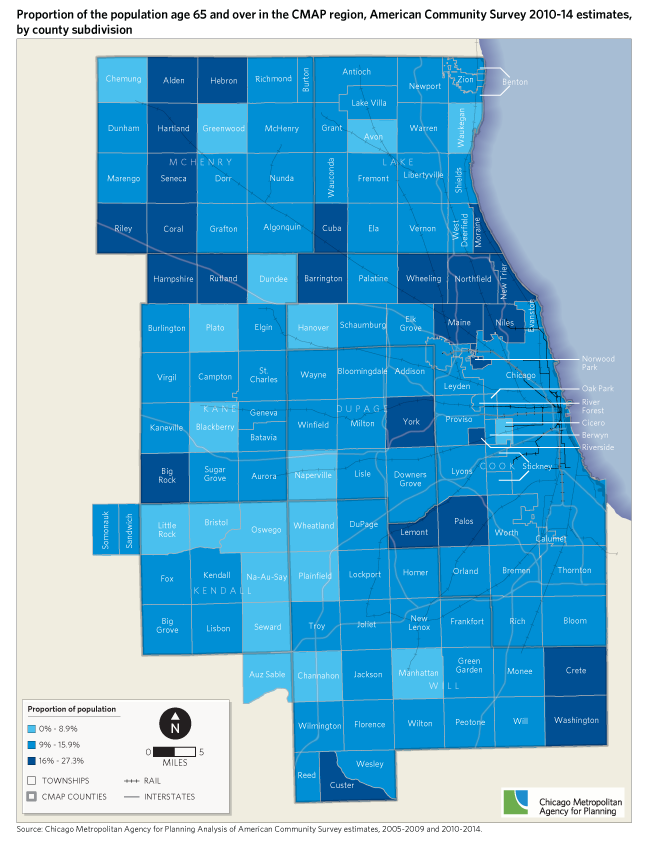
While most of the region's counties are very similar to the region as a whole in terms of the proportion of the population that are age 65 and over, concentrations of seniors can vary greatly across the region. The following map provides an overview of the proportion of the population that is age 65 and over by county subdivision (townships) in 2014. The 25 townships with higher proportions of seniors are most concentrated in north and far west areas of the region. Areas with a higher proportion of seniors include many inner ring suburban areas as well as less densely populated areas. The areas of the region with comparatively low proportions of seniors were primarily in the fast growing far southwestern portion of the region.
Most areas of the region only experienced a small increase of less than 3 percentage points in proportion of residents age 65 and over between 2009 and 2014. The region as a whole experienced an increase of 1 percentage point. However, some areas of the region (24 townships) actually experienced decreases in the proportion of seniors, including some areas with relatively high concentrations of that age group. The following map illustrates the change in proportion of the senior population between 2009 and 2014, by county subdivision (township).
Looking forward
GO TO 2040 includes recommendations to enhance the livability of the region's communities, which can also allow older residents to age in place. Communities must plan for enhanced transit networks, expanded services, and a changed housing stock to best support the region's aging population. Mixed-use centers, with a variety of services and essential activities within easy walking distance are also an important component of planning for residents at all stages of life.
CMAP's Local Technical Assistance (LTA) program promotes age-friendly planning through recommendations that help realize GO TO 2040's livability goals, and also helps residents plan for changing populations through the Homes for a Changing Region program. As the region begins work on the next comprehensive long-range plan, CMAP is examining strategies to help communities continue to plan proactively and prepare for the needs of seniors, and to protect the wellbeing of vulnerable residents. In addition, CMAP will be releasing a demographics snapshot analyzing changes in the region's population in the first half of 2016.